Caddy Webserver
Synopsis
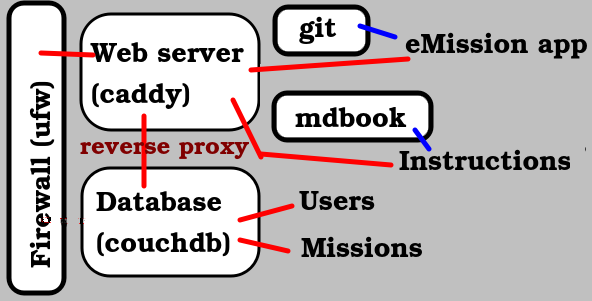
The caddy webserver will serve both application, web pages, and indirectly data from the database. It will also automatically aquired and keep current security certificates allowing secure SSL communication.
Installation
If you've been following these instructions sequentially, caddy should be already installed.
Configuration
Caddy is configured by a Caddyfile at /etc/caddy/Caddyfile
Initial contents:
# The Caddyfile is an easy way to configure your Caddy web server.
#
# Unless the file starts with a global options block, the first
# uncommented line is always the address of your site.
#
# To use your own domain name (with automatic HTTPS), first make
# sure your domain's A/AAAA DNS records are properly pointed to
# this machine's public IP, then replace ":80" below with your
# domain name.
:80 {
# Set this path to your site's directory.
root * /usr/share/caddy
# Enable the static file server.
file_server
# Another common task is to set up a reverse proxy:
# reverse_proxy localhost:8080
# Or serve a PHP site through php-fpm:
# php_fastcgi localhost:9000
}
Edit or copy /etc/caddy/Caddyfileto:
domain_name {
# Set this path to your site's directory.
root * /srv/www
# Enable the static file server.
file_server
}
domain_name:5984 {
reverse_proxy localhost:15984
}
domain_name:6984 {
reverse_proxy localhost:15984
}
Where domain_name is your actual chosen domain_name
Startup
caddy fmt --overwrite /etc/caddy/Caddyfile
systemctl enable caddy
systemctl status caddy
Test -- web service
From your web browser go to address domain-name (your chosen domain name)
Test -- database service
From your web browser go to address domain-name:6984/_utils/ (using your chosen domain name)